Vestel Electronics continuously searches for new ideas to develop new products and technologies with the help of innovation and R&D activities. It keeps close ties with Universities and other research centers. In this respect they are in cooperation with Ege University Science and Technology Centre (EBILTEM) in Izmir. EBILTEM as an interface organization of Ege University, is an internationally recognized university-industry collaboration institution housing a wide range of offices and units providing information, technology, IPR and innovation management support to industry. As a result of its technology transfer activities, it has been selected as the best performing centre by the European Commission in 2008. It is also cited in UNESCO Science Report 2010. Vestel Electronics and EBILTEM are also partners in Western Anatolian Information Technologies and Electronics Regional Innovation Centre (BATI-BINOM) project aiming to boost the R&D and innovation potential of the region in information technologies and electronics.
Access to knowledge is crucial
Mr. Metin Nil, the R&D Director of Vestel Electronics believes that knowledge is the main input for technology development. Vestel R&D centers closely follow the European technology platforms and project calls of European Union Seventh Framework Program (FP7) and show intensive effort to be partner in these projects. He says “easy access to knowledge is very important, but another important thing is the capacity of the knowledge absorption. The company has to have the maturity to exploit the opportunities. Collaboration with research institutions and Universities create an awareness that enables a company to identify the right opportunity.”
University-Industry cooperation and EBILTEM
EBILTEM, known as a “Gateway to Knowledge” by companies in Turkey, acts as an interface to direct Vestel Electronics’ open innovation efforts by providing ideas, information, network connections and resources. Prof. Vardar-Sukan who is the Director of EBILTEM says, “Technology protection and all IP issues are also vitally important subjects for a well-known technology company such as Vestel Electronics. Therefore, Vestel Electronics has established very close ties with EBILTEM Relay Centre of the European Patent Office, utilizing its services for patent searches, competitor analyses and technology watch. All these free of charge services have helped Vestel Electronics and EBILTEM to build an efficient university-industry cooperation model and have established fruitful and long lasting bridges between the two institutions.”
Mr. Metin Nil, states that EBILTEM has been one of the main sources of information, knowledge and networking for Vestel Electronics, throughout the years. “Through this cooperation, we never miss new ideas and opportunities. Vestel Electronics receives new project ideas, and technologies developed by the researchers in the universities via EBILTEM on weekly basis. Vestel Electronics also has access to EBILTEM’s Network for international technology, business and research opportunities. With the help of these facilities, Vestel Electronics has easy and fast access to Enterprise Europe Network profile database where they can see new technology, business and research offers and requests. This cooperation allows Vestel Electronics to reach all EU research calls and partner searches on time.”
Multinational projects
With such cooperation Vestel Electronics participated in an international joint research project entitled “Magneto”. The project was a Celtic initiative, a European research and development programme designed to strengthen Europe’s competitiveness in telecommunications. In Magneto project Vestel Electronics became a partner in a consortium of internationally well-known universities and companies from Austria, Canada, France, Ireland, Spain and Sweden.
Magneto, an acronym for; Management of the Outer Edge, provides a new level of service assurance and network management support to the “Outer Edge” domain i.e. the point of attachment of home area networks and other restricted area networks to help Operators, OEMs and Service Providers to deal with the increasing complexity and ever increasing number of connections at the Outer Edge. We define Outer Edge as “user networks” such as Home Area Networks, Small-Office, Hotel networks etc. These networks are attached to operator’s network through the access network but operators do not have direct or full control of these Outer Edge networks.
This 30 month long project was successfully completed in March of 2011, delivering an innovative and autonomic outer edge management solution and a new framework. Results have been internationally disseminated and companies including consortium members are utilizing this research in existing and new products.
Magneto’s main focus
The main focus of Magneto was to develop an innovative Network and Service management framework that enables integrated service and network management for outer edge devices in emerging networks. The Magneto framework enabled the management of home networks to be incorporated into telecommunication service provider management systems to provide end-to-end service management. The framework facilitated the scalability of the management systems to scale to deal with the expansion into millions of connected outer edge networks using an autonomic approach to self management. Magneto has developed novel solutions to service and network management to help operators meet the challenges posed by the outer edge in a secure manner. In particular Magneto has delivered a scenario based architecture and software proof of concept in the areas of service configuration and assurance, supported by an Autonomic framework for self management of outer edge devices.
Approach
Magneto has implemented the use of intelligent systems and process automation in its Autonomic framework to minimize human intervention at the outer edge. Inherent in this approach is a greatly increased emphasis on security and Magneto has adopted an end-to end approach to incorporating security in all aspects of the system. Magneto is access network neutral and can be applied in both fixed and mobile networks. A number of service based scenarios in the context of consumer demand for ‘Anytime, Anywhere’ Omnipresent Virtual Networks (OVNs) have formed the basis of its approach including:
- User subscription and OVN creation. This deals with subscription process to OVN service and creating a specific OVN for a user.
- Joining and content sharing. Once an OVN is created other users can join that specific OVN and share content among other users in the OVN
- Service Breakdown. This topic deals with fault management; more precisely probabilistic fault identification
- Service Quality Degradation. This aspect covers scenarios where the service quality is degraded and monitoring of service quality levels and SLA in such situations
- Device addition to an existing session. Users can add devices to an OVN and the OVN should recognize the newly added device; in addition existing service sessions should be portable to other capable devices.
- Real-time sharing. Sharing of external content between OVN initiator within his HAN and another OVN user.
Magneto has developed a common management framework to address these scenarios and prototypes have been demonstrated for the major scenarios.
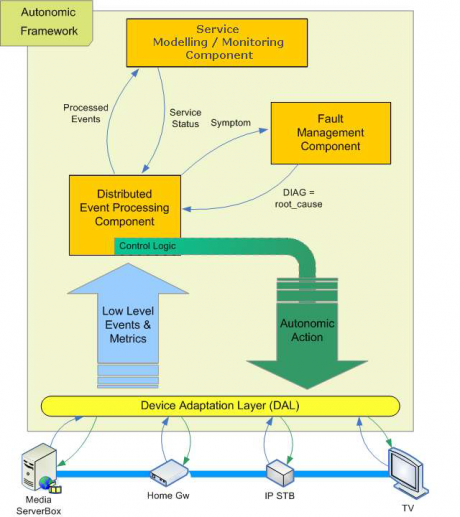
Achieved results
Magneto has developed an Autonomic framework for Outer Edge management, which allows easier service specification and deployment and reduces management costs (OPEX) and help operators meet the challenges posed by the outer edge. The project has delivered a new management solution which integrates the outer edge as a network and service centric component addressing Omnipresent Virtual Network services.
For service providers, especially convergent ones, the outer edge is becoming the unique service portal which allows the customers access to a huge variety of services.
The technological innovations in Magneto particularly address:
- Extension of self – management principles to the outer edge, e.g. the management of home area networks can be autonomic,
- Application of probabilistic techniques to deal with the very large and increasing levels of data that must be analysed for efficient service assurance,
- Implementation of Complex Event Processing and correlation of data and events for service assurance in a decentralized way, close to the event location,
- Quality of Service (QoS) estimation using lower level Network Key Performance Indicators (N- KPIs).
The Magneto design of an innovative and autonomic outer edge management solution and its integration of the outer edge management in a global management framework provide service providers with a global and innovative solution for end-to-end management of multimedia services. The Magneto autonomic framework provides an integrated approach to network and service management and proposes a fundamental change to the way that networks and services are managed at the outer edge.
Impact
Research results from the Magneto project have been reviewed and accepted by the Research community through journal and book publications and at major conferences including IMS 2010, BcN 2010, MACE 2010 and IM 2011.
Results from Magneto have been disseminated through contacts with the Autonomic Future Internet (AFI) and Measurement Ontology for IP traffic (MOI) industry specification groups at ETSI, and Magneto partners have participated in a panel discussion at TMF.
By carrying out the work at international level, the results of the Magneto project offers an opportunity for European companies to take a lead in outer edge management. The diversity of the partners taking part in Magneto, facilitates the exploitation and dissemination of the results across Europe and beyond, and will maximize the intellectual and commercial potential of the project. Magneto industrial partners are currently considering the commercial impact of the concepts on existing product roadmaps and the introduction of new products based on the research results.
Vestel Electronics’ contribution
- End user devices testing and manufacturing by Vestel and Blusens Companies
- Specification of the test environment
- Adaptation to the Magneto prototypes
- Dissemination Activities
- Autonomic computing (self-configuration, self-healing)
- Meetings and discussion with Universities
- Involved in project management and all work packages
Vestel Electronics’ project output
- Set Top Box
![]()

– Vestel MAGNETO4800 Device
Project impact to Vestel Electronics
The technology and background obtained from the Magneto project was transferred to Vestel Electronics’ data bank for use in other research by the R&D group and for the training of employees in related departments. R&D department was expanded with new engineers hired through the project. Vestel Electronics has used outer edge management technology, the developed communication mechanism and the know-how obtained in other projects as well:
- Connected TV: New generation connected TV that adds broadband connection, IPTV, and internet access to LCD and LED televisions.
- The software module developed for Magneto by Vestel is used in TV and Set Top Box projects enabling television set to receive and decode digital television (DTV) broadcasts from cable, satellite or other digital sources.
- New prototypes were developed including IPTV prototype for the Magneto project.
Vestel Electronics as a Consumer Electronics and R&D company plans shape long term roadmap in heterogeneous home networks and products that are closely related with this project such as wireless digital media adapters, IPTV set top boxes, IDTVs. Vestel Electronics also aims to use the Magneto knowledge and vision in all R&D projects and plans to have innovative consumer electronics devices that work seamlessly in home networks. The company believes that the output of Magneto project on Vestel products will be a big advantage at the market.
Conclusions
Success of Vestel Electronics is directly related to its dedication to innovation, to the high-quality research carried on in its large R&D centers and to its connections to national and international research organizations.
Vestel Electronics’ focus on innovation, forces it to extend research efforts beyond the company facilities. Cooperation with local and national universities, partnering on regional projects opens doors to new developments and research. International collaboration allows the company to work with other successful organizations and collective research not only provides valuable information but also new product and market partnerships.
Multinational projects like Magneto bring the research power from different countries together to advance in new technologies. Vestel Electronics continues to be a global consumer electronics manufacturer by applying these technologies to the processes and products.
Vestel Electronics could never have been part of a large project such as the Magneto project if it had not made the right investment into R&D throughout the years and if it had not established the right connections with academia and international organizations. It owes its competitive edge to the R&D awareness it has created at all levels of its management, production and sales departments.
Vestel Electronics should set an example to all companies, with sophisticated targets in internationalization. Regardless of size, geography and nationality, all companies benefit from new ideas. Those with ambitious objectives must be in search of new information within and outside of the borders. R&D departments can expand existing capabilities with the information obtained from open innovation, and create new products and businesses. National and international funds, interface organizations such as EBILTEM facilitating university collaboration are vital to open innovation. Such support systems need to be expanded and companies must benefit from them.
By Reha S. Senturk
 About Vestel Electronics
About Vestel Electronics
Vestel Group is comprised of 22 companies operating in manufacturing, technology development, marketing, and distribution areas in the consumer electronics, digital technologies, and household appliances industry. It is located in Manisa, Turkey. With 12 million units of production a year, Vestel Electronics is the largest television manufacturer in Europe. The company controls 6% of the worldwide, and 26% of the European TV market.
R&D facilities are located in Manisa, Izmir, UK, USA, Hong Kong, and Taiwan, employing the highest caliber engineers developing hardware and software solutions to provide clients with world class quality products. Exporting 96% of its production to 132 countries and realizing over 2 billion Euros of export revenues, Vestel became the export leader in Turkey. This revenue stream combined with the Group’s rapid growth in international markets has established Vestel as one of the worldwide consumer electronics leaders.
Vestel Electronics’ R&D activities in 2006 were carried out at the Main, High-End and Digital centers in Manisa, Izmir, Istanbul, Bristol and San Diego. Currently, Vestel R&D activities are carried out by specialized project groups individually responsible for the different aspects of industrial design, mechanical design, mechanical production, industrial applications, intellectual property rights and contracts, design verification, and hardware and software engineering. Vestel also works on a user interface customization (UI) solution based on SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics) definitions of UI designs, which enables quick customizations and different look and feel for different customers. One of the major successes of the company was the implementation of digital TV software with the addition of TV controls to the existing DVB software stack.
About the author
 Reha S. Senturk is a project manager of the internationally recognized university-industry collaboration institution Ege University Science and Technology Centre (EBILTEM) in Izmir, Turkey.
Reha S. Senturk is a project manager of the internationally recognized university-industry collaboration institution Ege University Science and Technology Centre (EBILTEM) in Izmir, Turkey.
He currently manages Western Anatolian Information and Electronics Regional Innovation Centre (BATI-BINOM), helping to create opportunities for innovation through partnerships, financial support, and implementation of new ideas or products, thereby nourishing the R&D and innovation power of the industry in the region.
Contributing editor
 This article was sourced and co-edited by Terry Young, who has 25 years experience in innovation management. He is President Emeritus of the Association of University Technology Managers (AUTM ). He has extensive experience in expert services internationally, with more than 60 trips abroad. He is currently President of Beyond the First World Corporation.
This article was sourced and co-edited by Terry Young, who has 25 years experience in innovation management. He is President Emeritus of the Association of University Technology Managers (AUTM ). He has extensive experience in expert services internationally, with more than 60 trips abroad. He is currently President of Beyond the First World Corporation.







