“Big Data” is a term encompassing the use of techniques to capture, process, analyze and visualize potentially large datasets in a reasonable timeframe not accessible to standard IT technologies. By extension, the platform, tools and software used for this purpose are collectively called big data technologies.
Big data techniques complement business intelligence (BI) tools to unlock value from enterprise information. Whereas BI traditionally performs structured analysis and provides a rear-view mirror into business performance, big data analytics provides a forward-looking view, enabling organizations to anticipate and execute on opportunities of the future
Characteristics of Big Data
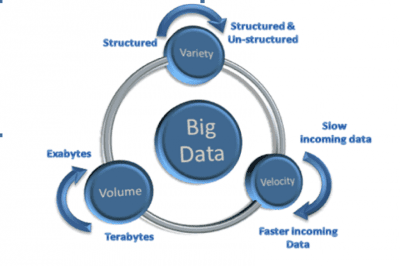
Big data is not just about the size of data but also includes data variety and data velocity. Together, these three attributes form the V’s of big data as shown by Fig 1.
Volume
“Volume” is synonymous with the “big” in the term big data. Volume is a relative term—some smaller-sized organizations are likely to have mere gigabytes or terabytes of data storage as opposed to the petabytes or exabytes of data that big global enterprises have. Data volume will continue to grow regardless of the organization’s size. There is a natural tendency for companies to store data of all sorts: financial data, medical data, environmental data and so on. Many of these companies’ datasets are within the terabytes range today, soon they could reach petabytes or even exabytes.
Variety
Data can come from a variety of sources (typically both internal and external to an organization) and in a variety of types. With the explosion of sensors and smart devices as well as social networking, data in an enterprise has become complex because it includes not only structured traditional relational data, but also semi-structured and unstructured data.
Velocity
The velocity of data in terms of the frequency of its generation and delivery is also a characteristic of big data. Conventional understanding of velocity typically considers how quickly the data arrives and is stored and how quickly it can be retrieved. In the context of big data, velocity should also be applied to data in motion: the speed at which the data is flowing.
Fig: The 3 V’s of Big Data
How Can Your Business Benefit from Big Data?
1. Faster and better decision making
This is probably the biggest benefit of big data. The quality of the data, and the speed of generating the data allows business executives to make more informed decisions, and to make these decisions quicker. Good, fast decisions are particularly important in highly competitive industries. As an example, United Healthcare, a health insurance giant in the U.S., uses big data to gauge customer experience. It converts voice calls into text and looks for indicators if the customer was satisfied or dissatisfied.
2. Product development
Many businesses both online and offline are using big data in product development. As an example, the Phoenix Suns NBA team used Verizon’s Precision Market Insight generated using big data for info on where people attending the team’s games live, the percentage of attendees who are not from Phoenix, how often attendees visit fast food chains and other information to help with the team’s promotion and advertising campaigns.
3. Timely access to data
Research shows that workers spend up to 60% of each workday managing and attempting to find the right data. Big data, therefore, helps improve productivity. Studies show that senior executives find accessing the right data to be difficult.
4. Cost benefits
Big data technologies are cheaper than traditional architectures like data warehouses and marts. Although it is difficult to compare big data with traditional architectures because they have different functionalities, a price comparison suggests order-of-magnitude improvements. Most big companies today are using big data alongside existing architecture, but the trend is towards the former. Consider outsourcing big data and other services like database management to an Oracle remote DBA to save money (you will not have to hire an in-house team for the job).
5. Holistic data
Most organizations keep information in silos. As an example, marketing data can be found in web analytics, social analytics, mobile analytics, A/B Testing tools, CRMs and email marketing systems, each focusing on its own silo.
6. Trustworthy data
Poor quality data can be very expensive. Simple things like monitoring multiple systems to get customer contact info can save your business millions of dollars.
7. Relevant data
Most companies say they are dissatisfied with the ability of the tools they use to filter out irrelevant data. Filtering such simple things as customers from web analytics provides a ton of insight that is useful in your acquisition efforts.
8. Data security
Data security breaches are very expensive. Not only do you lose customers, but you might end up spending huge amounts of money in lawsuits and in redesigning your website’s security. Big data technology and hosting partners give you a secure infrastructure. Big data tools allow you to map the entire data landscape, thereby allowing you to analyze internal threats. As an example, big data analytics allows you to flag 16-digit numbers—potentially credit card numbers—to prevent credit card fraud.
9. Authoritative data
Most companies have several versions of truth depending on the data source. Big data allows companies to combine different, vetted data sources, which means the data generated will be highly accurate.
10. Actionable data
Studies show that almost half the companies that use outdated or bad data end up making bad decisions that are very costly. A good example of how big data is actionable is Delta: their baggage tracking app powered by big data allows customers to keep track of their baggage, leading to greater brand loyalty.
11. Risk analysis
There are many social and economic factors that determine the success of a business. Big data allows for predictive analysis—you are able to analyze social media feed and newspaper reports so that you can take preventive measures where need be. Big data also allows you to perform detailed health-tests on your customers and suppliers.
12. New revenue streams
You can sell the data you generate using big data analytics to interested parties. As an example, if you have a fashion stall in a shopping mall, you could sell customer behavior data to distributors, manufacturers and other interested parties.
13. Real-time website customization
Once you have customer preference from big data analytics, you can personalize the look and feel of your website to suit individual customers in real-time. As an example, you could personalize your website based on gender and nationality. Another good example is Skillsoft, which has been using big data to individualize content based on surveys and direct email response behavior.
Another good example of how a business can use big data to improve its operations and increase its margins is CaixaBank, a Spanish retail bank and insurer with close to 14 million customers, over 5,000 branches and close to 10,000 ATMs. According to Luis Esteban Grifoll, the bank’s CEO, the bank was facing several challenges that big data has helped solve:
- Difficulty integrating data from the vast branch and ATM network and from mobile and internet banking: Oracle big data allows the bank to understand the customer better and to offer personalized banking solutions, thereby gaining customer loyalty and improving business competitiveness.
- Difficulty messaging customers: Big data allows the bank to effectively communicate with customers on such things as new bank services and products.
- Expensive and complex data extraction and transformation: Big data ensures that these processes are flexible and agile, enabling the bank to quickly analyze, adapt, decide and act on improving time-to-market.
- Difficulty accessing non-sensitive information: The bank, thanks to big data, is now able to provide employees with access to info that is not too sensitive. This information helps promote creativity and innovation and helps improve productivity.
The fact that eBay, Google and LinkedIn have been using big data since the concept was introduced is proof that there is something to be gained.
By Sujain Thomas
About the author
 Sujain Thomas is a data IT professional who works closely with DBA experts to provide her clients with fantastic solutions to their data problems. If you need data IT solutions, she is the person for the job. She has contributed articles on business2community.com, sociable.co and many more.
Sujain Thomas is a data IT professional who works closely with DBA experts to provide her clients with fantastic solutions to their data problems. If you need data IT solutions, she is the person for the job. She has contributed articles on business2community.com, sociable.co and many more.
Email: thomassujain@gmail.com
Twitter: @sujainthomas
LinkedIn Profile
Further Reading
Ten Practical Big Data Benefits
20 Examples of ROI and Results with Big Data
Featured image via Yayimages.







